Introduction:
Navigating through Android apps is a crucial aspect of user experience. In this blog post, we'll dive into the world of Navigation Component and explore how it simplifies the navigation process in Android app development.
Section 1: Understanding Kotlin Navigation Component:
Kotlin Navigation Component is a part of the Android Jetpack library that provides a framework for navigating between different parts of your app. It simplifies the implementation of navigation and ensures a consistent and predictable user experience.
Section 2: Setting Up Kotlin Navigation Component:
To get started, add the following dependencies to your build.gradle file:
implementation "androidx.navigation:navigation-fragment-ktx:2.4.0"
implementation "androidx.navigation:navigation-ui-ktx:2.4.0"
Now, configure the navigation component in your MainActivity:
class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
private lateinit var navController: NavController
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main)
val navHostFragment =
supportFragmentManager.findFragmentById(R.id.nav_host_fragment) as NavHostFragment
navController = navHostFragment.navController
setupActionBarWithNavController(navController)
}
override fun onSupportNavigateUp(): Boolean {
return navController.navigateUp() || super.onSupportNavigateUp()
}
}
Section 3: Creating a Navigation Graph:
Create a navigation graph by adding a nav_graph.xml file to the res/navigation directory. Define your destinations, actions, and fragments in the visual navigation editor.
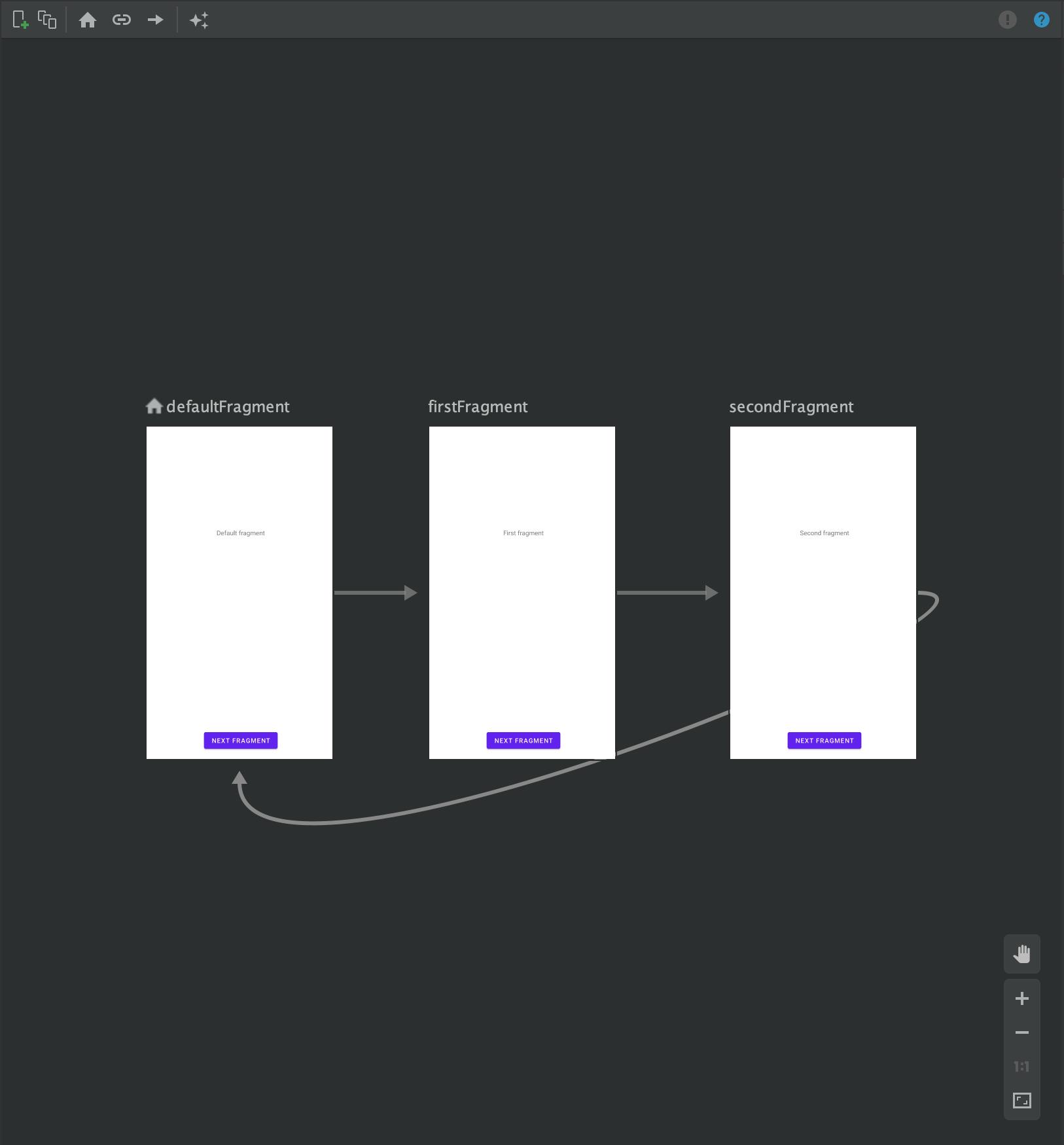
<!-- res/navigation/nav_graph.xml -->
<navigation xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:id="@+id/nav_graph"
app:startDestination="@id/firstFragment">
<fragment
android:id="@+id/firstFragment"
android:name="com.example.FirstFragment"
android:label="fragment_first"
tools:layout="@layout/fragment_first" />
<fragment
android:id="@+id/secondFragment"
android:name="com.example.SecondFragment"
android:label="fragment_second"
tools:layout="@layout/fragment_second" />
<!-- Add more fragments and actions as needed -->
</navigation>
Section 4: Navigating Between Destinations:
Navigate between destinations using the NavController:
// Inside a fragment or activity
val action = FirstFragmentDirections.actionFirstFragmentToSecondFragment()
navController.navigate(action)
Section 5: Deep Linking with Kotlin Navigation Component:
Enable deep linking by adding the following to your navigation graph:
<deepLink app:uri="yourapp://host/secondFragment" />
Handle deep links in your MainActivity:
val navController = findNavController(R.id.nav_host_fragment)
val deepLink = findNavController(R.id.nav_host_fragment).createDeepLink()
.setDestination(R.id.secondFragment)
.createPendingIntent()
// Set up PendingIntent with deepLink in Notification or other components
Section 6: Handling Up and Back Navigation:
The Up button and Back button behavior is automatically handled by the navigation component. Customize it using the OnBackPressedDispatcher:
override fun onBackPressed() {
if (!navController.navigateUp()) {
super.onBackPressed()
}
}
Section 7: Testing and Debugging Navigation:
Test navigation using the NavController and ensure proper handling of back and up navigation. Use the Navigation Test library for comprehensive testing.
Conclusion:
Navigation Component streamlines the navigation process in Android development, making it more intuitive and developer-friendly. Experiment with it in your projects and share your experiences!

